Understanding Opioid Detection Time
Opioid detection time is a crucial concept to grasp, especially in today’s world where opioid use is rampant. It refers to the duration opioids can be detected in a person’s system. This knowledge is vital in various scenarios, such as drug testing, monitoring treatment progress, and ensuring safety in correctional facilities.
Several factors can influence the detection time of opioids. These include the type and dosage of the opioid, the individual’s metabolism, and their overall health and body composition. For instance, a person with a faster metabolism might eliminate opioids from their system quicker than someone with a slower metabolism.
It’s important to remember that not all substances detected in drug tests are opioids. For example, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has reported a significant increase in detections of xylazine, a powerful sedative used by veterinarians.
However, xylazine is not an opioid and cannot be reversed with Narcan, a medication used to reverse opioid overdose.
The rise in xylazine detections is alarming, given its gruesome side effects and resistance to standard opioid overdose treatments. Nicknamed the “zombie drug,” xylazine has been found in illicit drug combinations, leading to several deaths.
To address the issue of xylazine, bipartisan legislation called the TRANQ Research Act (H.R. 1734) has been introduced in the House of Representatives. This act aims to increase research and analysis on xylazine and its impact on public health.
In conclusion, understanding opioid detection time and the factors that affect it is crucial. It’s also important to be aware of other substances like xylazine that may be present in illicit drug combinations. Stay informed, stay safe.
Opioid Detection in Different Biological Samples
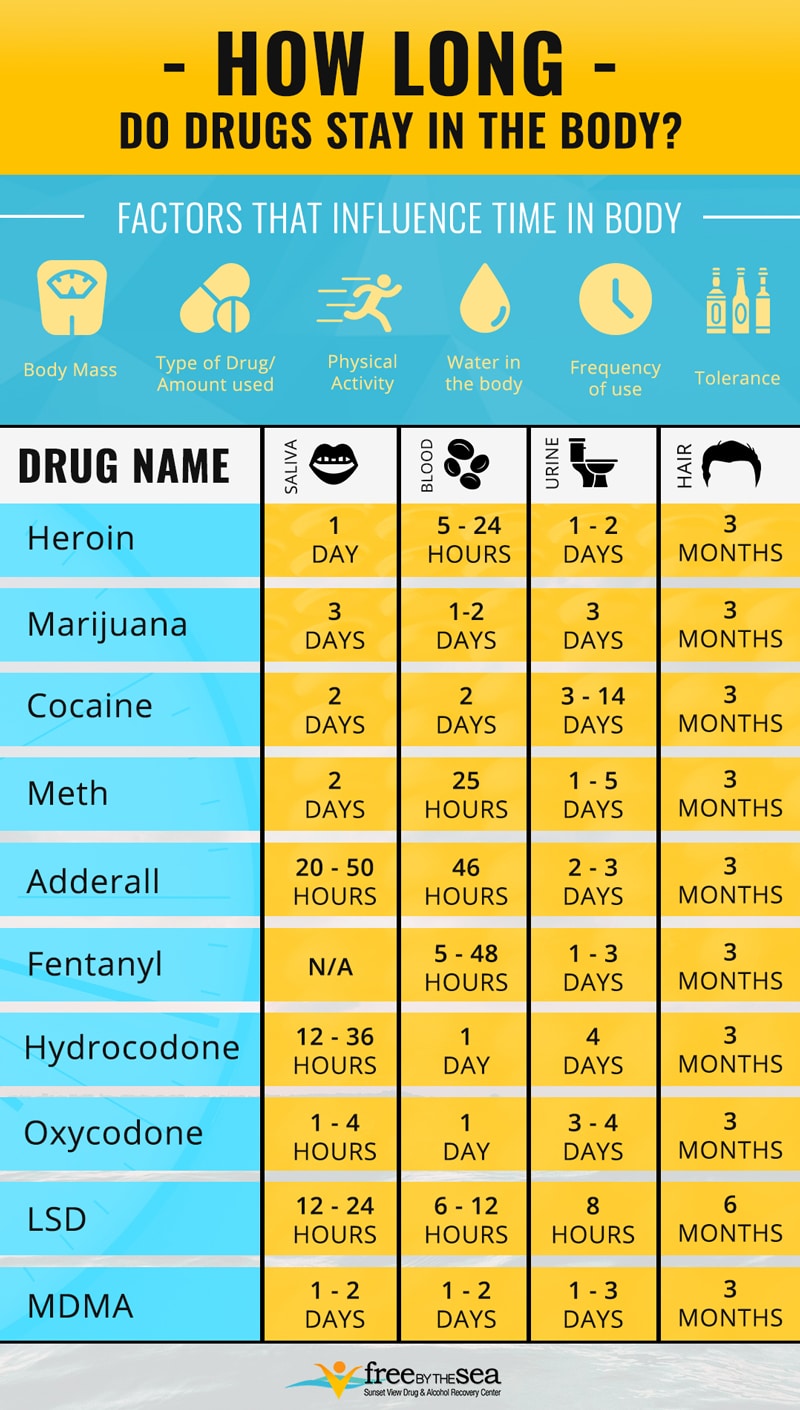
Opioids can be detected in several biological samples. Each type of sample offers a unique detection window. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Urine Samples
Urine samples are commonly used for opioid detection. They can reveal opioid use for 1-3 days after consumption. This short detection window makes urine testing valuable for monitoring patients undergoing treatment, such as with buprenorphine. However, it’s important to note that some patients may alter their urine samples, indicating illicit drug use.
Blood Samples
Blood samples offer a detection time of up to 24 hours. Though the window is shorter, blood tests can provide immediate and accurate results.
Saliva Samples
Saliva samples can detect opioids for 1-4 days. The U.S.

Department of Transportation has approved oral fluid testing for drug testing in regulated industries. This method offers direct observation and immediate detection of recent drug use.
Hair Samples
Hair samples provide the longest detection window of up to 90 days. This makes hair testing particularly useful for long-term monitoring of drug use.
Remember, the detection times can vary depending on the type of opioid and the individual’s metabolism. It’s crucial to understand these detection windows, especially if you’re an employer deciding between urine or oral fluid tests for DOT-regulated drug tests.
With the rise of illicit drugs and their impact on health and security, opioid detection plays a crucial role in monitoring and addressing substance abuse. As we navigate this challenging landscape, it’s important to stay informed and updated on drug testing policies and procedures.
For more information on drug detection tools, check out this article by the FDA and NIH. Stay safe and informed!
Common Misconceptions About Opioid Detection
When it comes to opioid detection, there’s a lot of misinformation floating around. One of the most common misconceptions is that all opioids have the same detection window. This couldn’t be further from the truth. Different opioids have different detection windows, meaning they can be detected in the body for different lengths of time.
Not One Size Fits All
For instance, morphine, a natural opioid, can be detected in urine for up to three days. On the other hand, fentanyl, a synthetic opioid, has a much shorter detection window. It can be detected in urine for up to 72 hours after use. So, it’s clear that not all opioids are created equal when it comes to detection.
The Danger of Misinformation
Another dangerous misconception is that opioid detection is a simple process. In reality, it requires expertise from forensic science, pharmacology, chemistry, and biochemistry. It’s not as simple as taking a quick test. Opioid detection methods include immunoassays, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).

Trust the Experts
If you’re concerned about opioid use, it’s best to trust the experts. Companies like Quest Diagnostics offer reliable opioid detection services. They use advanced technology to improve the reliability of their detection methods.
Stay Informed
Staying informed about the realities of opioid detection can help prevent misuse and addiction. It’s essential to understand that opioid detection is a complex process, and different opioids have different detection windows. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to combating the opioid crisis.
Don’t Be Fooled
Lastly, don’t be fooled by the belief that opioids can’t be detected if they’re mixed with other substances. Even if opioids like fentanyl are mixed with adulterants like xylazine, naloxone can still reverse their effects in overdoses.
In the fight against the opioid crisis, accurate information is our most potent weapon. Let’s use it wisely.
How Long Do Opioids Stay in Your System?
Opioids, whether prescription painkillers like oxycodone and hydrocodone or illicit drugs like heroin, have a significant impact on our bodies. They work by attaching to specific receptors in the brain, blocking pain signals. However, misuse can lead to addiction, making opioids a major public health concern.
How Long Do They Stay?
The duration of opioids in a person’s system varies. It depends on the type of opioid and the biological sample tested. For instance, heroin can be detected in urine for 1-3 days, while methadone stays for 1-7 days. These detection windows can change based on factors like the amount of opioid use, individual metabolism, and the sensitivity of the testing method.
Testing Methods
There are several ways to test for opioids. Urine testing is the most common, detecting opioids for 1-3 days after use. Blood tests have a shorter detection window, typically a few hours to a day. Saliva tests can detect opioids for up to 1-4 days. Hair tests, on the other hand, can detect opioids for up to 90 days after use.
It’s important to remember that these detection windows are approximate. They can vary based on individual factors.
Addressing the Opioid Crisis
The opioid crisis is a significant public health concern. Overdose deaths involving opioids have been on the rise. The National Institute on Drug Abuse are working tirelessly to combat this issue.
Treatment options for opioid addiction include medication-assisted treatments like methadone or buprenorphine. These treatments, combined with counseling and behavioral therapies, can effectively treat opioid addiction.
Emerging Threats
The Office of National Drug Control Policy has declared fentanyl-adulterated or -associated xylazine an “emerging threat” to the country. Xylazine, a powerful sedative used by veterinarians, has been detected in illicit fentanyl supplies in Texas and has caused deaths.
In response, legislation called the TRANQ Research Act has been introduced in the House of Representatives. This act aims to address the growing concern of xylazine use and its impact on public health.
Stay Informed
Understanding how long opioids stay in your system can help you make informed decisions about your health. Stay informed, stay safe. For more information, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Implications of Opioid Detection
Understanding the detection of opioids in the human body has significant implications. It plays a crucial role in various fields like drug screenings, pain management, and addiction treatment programs.
Drug Screenings
In drug screenings, opioid detection information is vital. It helps to identify individuals who may be misusing opioids. This can be particularly useful in workplaces, schools, or sports organizations.
Pain Management
In the field of pain management, understanding opioid detection can help doctors monitor their patients. It can ensure that prescribed opioids are used correctly and not abused.
Addiction Treatment Programs
For addiction treatment programs, opioid detection is a crucial tool. It can help track a patient’s progress and verify their abstinence from opioids.
However, the fight against opioid misuse doesn’t stop here. Future developments in opioid detection are on the horizon. Ongoing research and advancements in this field are expected to bring about more accurate and efficient detection methods.
A recent case highlights the severity of the opioid crisis. The Southern and Eastern Districts of New York unsealed indictments charging China-based companies, including Harm Reduction Innovation Lab at Rhode Island Hospital is also making strides in developing interventions for people who use drugs.
Moreover, the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services is authorized to spend $39.2 million on evidence-based programming, treatment providers, recovery supports, harm-reduction strategies, and prevention programming. This funding comes from the initial settlement payments from the nationwide settlement with pharmaceutical distributors and opioid manufacturer Johnson and Johnson.
In the end, understanding opioid detection is not just about knowing how long opioids stay in your system. It’s about using this knowledge to combat the opioid crisis and save lives.
Conclusion: Opioid Detection Time
Understanding the detection time of opioids is crucial. It’s not just about knowing how long these substances stay in the system. It’s about grasping the depth of the opioid crisis we face today.
Opioids can linger in your system for days, even up to 90 days in hair samples. Factors like the type of opioid, individual metabolism, and method of administration can influence this.
It’s important to remember that detection doesn’t always indicate current use. Opioids like heroin, oxycodone, and fentanyl have different detection times.
The presence of opioids, especially potent ones like fentanyl, is a pressing issue. In Delaware alone, fentanyl accounts for over 80% of fatal overdoses. This crisis calls for immediate action and understanding.
Turning Knowledge into Action
Knowledge about opioid detection can be a tool for prevention and intervention. It can guide drug screenings and pain management strategies. It can also inform treatment programs for those struggling with addiction.



